The History of Nigeria | A Timeline
Nigeria is a West African nation with a rich history. The history of Nigeria spans centuries, from ancient times to today. The story of Nigeria is full of diverse cultures, strong leaders, and big events. These have shaped the country’s identity.

Nigeria’s history shows its resilience and the strong spirit of its people. We’ll look at the ancient civilizations that started it all. We’ll see how the colonial era changed the nation. And we’ll talk about the fight for independence that led to self-governance.
Join us as we explore Nigeria’s past, present, and future. It’s a story of a nation that has overcome many challenges.
Nigeria’s Ancient Roots and Diverse Ethnic Groups
Nigeria is a land full of cultural heritage. It has many ethnic groups that have made its history vibrant. From the northern Hausa-Fulani to the southeastern Igbo and the southwestern Yoruba, Nigeria’s mix of people shows its deep history.
Tracing the Origins of Nigeria’s Vibrant Cultures
The origins of Nigeria’s cultures go way back to pre-colonial empires and kingdoms. The Yoruba are famous for their art and festivals, tracing back to the Oyo Empire. The Igbo people have a history of democracy from the Nri Kingdom. These groups have mixed together to form a rich Nigerian culture that is both complex and interesting.
The Richness of Nigeria’s Pre-Colonial Kingdoms and Empires
- The Benin Empire was known for its bronze sculptures and advanced government before European rule.
- The Kanem-Bornu Empire covered parts of modern-day Nigeria, Chad, and Niger. It was a center of trade and Islamic learning.
- The Oyo Empire had a strong military and political system. It had a big impact in the Yoruba-speaking areas of Nigeria.
These pre-colonial kingdoms and empires set the stage for Nigeria’s cultural diversity. They showed the region’s deep political history and economic strength before European colonizers arrived.

The Arrival of European Colonizers and the Scramble for Africa
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Nigeria became a key spot in a global fight for power called the Scramble for Africa. European powers, especially the British, wanted to control Africa’s rich resources. They used military strength, diplomacy, and economic tactics to get a piece of the pie.
The British aimed to grow their economic and political reach. They created a strong colonial rule in Nigeria. This nigerian colonialism changed the political, economic, and social life of the area deeply.

Once in power, the British divided Nigeria into northern and southern parts. This move, called the Amalgamation of Northern and Southern Nigeria, created the modern Nigeria. But, it also caused resistance and anger among the locals because it changed their way of life.
The colonial time changed Nigeria’s economy a lot. The British wanted to use Nigeria’s resources and connect it to their global trade. This led to cash crops, new roads, and changes in laws and government.
The effects of nigerian colonialism are still debated today. It had both good and bad effects on Nigeria’s growth. Studying this period helps us understand Nigeria’s history, its current state, and what the future might hold.
The British Colonial Era and the Rise of Nationalism
The British Empire spread across Africa, putting Nigeria under colonial rule. In 1914, the British joined the Northern and Southern protectorates into one. This move created the modern Nigerian state but also made people want their own country.
The History of Nigeria: The Amalgamation of Northern and Southern Nigeria
Merging the Northern and Southern protectorates was a big change. Lord Lugard, Nigeria’s first Governor-General, made this decision. He wanted to make governance and economic growth easier.
But, this action showed the big cultural and political differences between the regions. It set the stage for future challenges.
The Struggle for Independence and the Emergence of Nigerian Leaders
As Nigeria’s economy grew, so did the wish for self-rule. Leaders like Nnamdi Azikiwe, Obafemi Awolowo, and Ahmadu Bello fought for independence. They used politics, civil disobedience, and negotiations to lead Nigeria to freedom in 1960.
The British colonial era was a key time in Nigeria’s history. It shaped its politics, economy, and society. The joining of the protectorates and the rise of nationalism led to Nigeria’s independence. This brought a new era of self-determination and national pride.
History of Nigeria: The Path to Independence and Beyond
Nigeria’s journey to independence was filled with both highs and lows. The Nigerian Civil War was a key event that deeply affected the nation. It was caused by tensions over ethnicity, politics, and economy that started during the colonial times.
History of Nigeria: The Nigerian Civil War and Its Lasting Impact
The Nigerian Civil War, also known as the Biafran War, started in 1967 and ended in 1970. It began when the southeastern region, Biafra, wanted to leave Nigeria. This was because the Igbo people felt left out and wanted more power.
The war was brutal, causing a lot of deaths and famine. Over 1 million Nigerians lost their lives, mostly civilians. This dark period in Nigeria’s history still affects its politics and society today.
- The Nigerian Civil War deeply changed the country’s politics and society.
- It made the federal government more powerful, taking power away from the regions.
- The war’s effects still affect Nigeria’s relationships between regions and ethnic groups.
- After the war, there was a push for national unity and more inclusive government.
After the war, Nigerians showed great strength. They started rebuilding their country and fixing their social ties. This process has had ups and downs, as Nigeria deals with its difficult past.

Nigeria’s Post-Independence Political Landscape
Since Nigeria became independent in 1960, it has faced many ups and downs in its push for democracy. The country has seen both military and civilian rule, each shaping its politics deeply.
History of Nigeria: Challenges and Triumphs of Nigerian Democracy
The early years were tough, with many military takeovers and power struggles. This led to long periods of military rule, causing economic and political problems. Yet, the Nigerian people’s strong wish for democracy led to a return to civilian rule in 1999.
Since then, Nigeria has worked hard to build a strong democracy. The country has seen peaceful handovers of power in elections, even with many hurdles. Issues like corruption, ethnic and religious tensions, and strong political leaders have sometimes threatened democracy.
- Periods of military rule and coups disrupted democracy.
- The Nigerian people’s resilience brought back civilian rule in 1999.
- Peaceful power changes through elections, despite challenges.
- Corruption, ethnic and religious tensions, and strong leaders have threatened democracy.
Despite the hurdles, Nigeria has seen big wins. It’s worked to improve its democracy, fight corruption, and tackle economic and social issues. Groups like civil society, the press, and active citizens have helped push democracy forward.

Nigeria is still working on making its democracy stronger. The people’s strength and a focus on better governance and development suggest a hopeful future for democracy.
History of Nigeria: The Richness of Nigerian Culture, Arts, and Heritage
Nigeria is the most populous country in Africa, known for its vibrant culture. It’s a place where nigerian culture, nigerian arts, and nigerian heritage shine brightly. The nation is a beacon of creativity and artistic expression.
Nigeria’s music is at the heart of its culture. You’ll find everything from Afrobeat to Highlife, music that has won fans all over the world. The country’s literature is just as strong, with authors like Chinua Achebe and Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie telling stories that explore Nigerian life deeply.
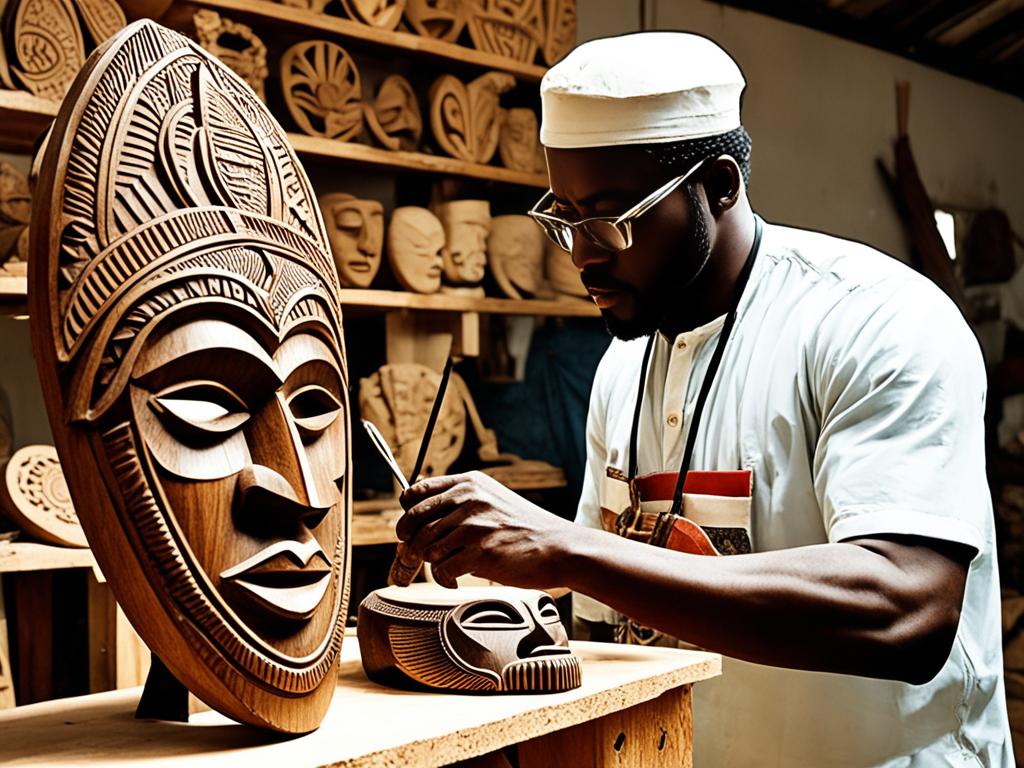

The visual arts in Nigeria are also a big deal. You’ll see vibrant paintings, sculptures, and textiles that show off the nation’s cultural heritage. The Adire fabrics from the Yoruba people and the bronze castings from the Benin Kingdom are just a few examples of Nigeria’s artistic talent.
Nigeria’s culture goes beyond music and art. It’s home to over 250 ethnic groups, each with their own traditions and beliefs. You can experience this through colorful festivals, lively street markets, and traditional stories. Nigeria’s nigerian heritage is a source of pride for its people.
Nigeria is a global center for art and culture. Its creative talents have made a mark worldwide, showing off the nigerian culture to the world. By preserving and celebrating its traditions, Nigeria ensures its heritage will last for many generations.
History of Nigeria: Nigeria’s Enduring Legacy and Future Prospects
Nigeria’s history shows us a nation with a deep and lasting impact. It has faced many challenges but has always come out strong. This shows its strength and its ability to grow.
The story of Nigeria tells us about the strength of different cultures and the human spirit. The Nigerian economy has faced ups and downs but keeps growing. The Nigerian geography is full of resources that will help the country grow in the future.
Looking ahead, Nigeria has a bright future but it will be complex. It needs to keep its culture while moving forward in a changing world. With strong leadership, good institutions, and the people’s spirit, Nigeria is ready to write its next chapter. This chapter will inspire people for years to come.
FAQ
What is the history of Nigeria?
Nigeria’s history is long and complex, spanning centuries. It was once home to ancient kingdoms and empires like the Oyo, Benin, and Kanem-Bornu. European colonizers, especially the British, arrived in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, changing Nigeria’s politics and economy. After fighting for independence, Nigeria became free from the UK in 1960. Since then, it has faced challenges in building a stable nation, dealing with political and economic issues.
What are the major ethnic groups in Nigeria?
Nigeria is known for its ethnic diversity, with over 250 groups. The Hausa-Fulani, Yoruba, and Igbo are the biggest and most influential groups. Other important groups include the Ijaw, Kanuri, Tiv, and Ibibio. Each group has its own language, culture, and traditions, adding to Nigeria’s rich society.
How was Nigeria affected by European colonialism?
European colonialism had a big impact on Nigeria. The British created the Colony and Protectorate of Nigeria in 1914, uniting diverse regions. This brought big changes to Nigeria’s politics, economy, and society. The British introduced policies like indirect rule and exploited resources, changing the economy and society. These changes also sparked Nigerian nationalism, leading to independence in 1960.
Who were the key leaders in Nigeria’s independence movement?
Key figures in Nigeria’s fight for independence were Nnamdi Azikiwe, Obafemi Awolowo, and Ahmadu Bello. Azikiwe was a leading nationalist and Nigeria’s first President. Awolowo was a Yoruba leader who supported a federal system for Nigeria. Bello was a Northern leader crucial to independence. These leaders worked hard to get Nigeria free from the UK.
What was the Nigerian Civil War, and what was its impact?
The Nigerian Civil War, also called the Biafran War, lasted from 1967 to 1970. It started when the Southeastern region, Biafra, tried to break away, led by Chukwuemeka Odumegwu Ojukwu. The war killed over a million Nigerians, mostly Igbo. It caused political and economic problems and deep divisions in society that still affect Nigeria today.
What are some of the key aspects of Nigerian culture and heritage?
Nigeria is known for its lively and diverse culture. It has a wide range of music, literature, arts, and traditions, each from different ethnic groups. Nigerian music, like Afrobeat and juju, is popular worldwide. Writers like Chinua Achebe and Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie have made a mark in literature. The country’s festivals, crafts, and food show its deep cultural identity.



Nigeria have a really great history, it’s culture and traditions portray alot
This post is a great resource for anyone looking to understand Nigeria’s complex history. Well done!”