
Business: All To Know Before Starting A Business

Business is a cornerstone of modern society, driving innovation, economic growth, and societal progress. At its core, business involves the creation, operation, and management of enterprises to provide goods and services to customers, with the aim of generating profit. This article explores the essential aspects of business, from its fundamental principles to strategic management, market dynamics, and future trends.
Types of Businesses
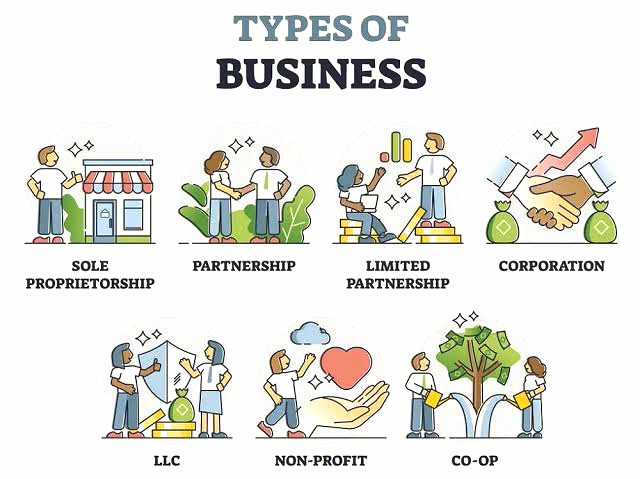
Businesses can be categorized into various types based on ownership structure, industry, and size:
- Sole Proprietorship: Owned and operated by a single individual. It is the simplest and most common form of business organization.
- Partnership: Involves two or more individuals who share ownership and management responsibilities.
- Corporation: A legal entity separate from its owners, offering limited liability to its shareholders.
- Limited Liability Company (LLC): Combines the benefits of a corporation and a partnership, providing limited liability while allowing flexible management.
- Non-Profit Organization: Operates to fulfill a charitable, educational, or social mission rather than generating profit.
Business Functions
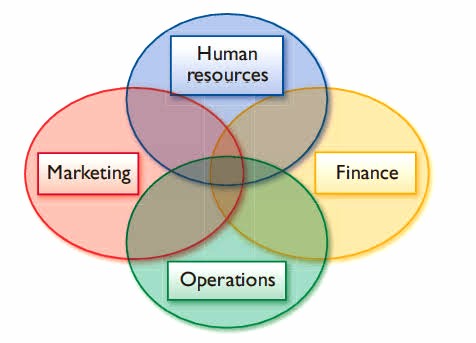
The operation of a business revolves around several key functions:
- Operations: Manages the process of production and delivery of goods or services.
- Marketing: Involves promoting and selling products or services, including market research and advertising.
- Finance: Manages the financial aspects, including budgeting, accounting, and investment.
- Human Resources: Focuses on recruitment, training, employee relations, and compensation.
- Sales: Engages directly with customers to sell products or services.
Strategic Management

Strategic management is crucial for long-term success and involves the following steps:
- Goal Setting: Defining clear, measurable objectives for the organization.
- Analysis: Conducting a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to understand internal and external factors.
- Strategy Formulation: Developing plans to achieve business goals, such as growth strategies, competitive positioning, and market entry tactics.
- Implementation: Executing the strategies through coordinated efforts across the organization.
- Evaluation: Monitoring progress and making adjustments as necessary to stay on track.
Market Dynamics

Understanding market dynamics is essential for any business. Key concepts include:
- Supply and Demand: The fundamental economic principle that describes the relationship between the availability of a product and the desire for that product.
- Market Segmentation: Dividing a market into distinct groups of consumers with common needs or characteristics.
- Competitive Analysis: Assessing competitors to identify strengths, weaknesses, and market position.
- Consumer Behavior: Studying how individuals make purchasing decisions to tailor marketing strategies effectively.
Financial Management

Sound financial management is the backbone of a sustainable business. Important aspects include:
- Accounting: Recording and reporting financial transactions to track business performance.
- Budgeting: Planning income and expenditure to ensure financial stability.
- Investment: Allocating resources to generate returns and drive growth.
- Financial Analysis: Using financial data to make informed business decisions.
Innovation and Technology

Innovation and technology play pivotal roles in modern business:
- Research and Development (R&D): Investing in new products and technologies to stay competitive.
- Information Technology (IT): Utilizing software and hardware to enhance business operations and communication.
- E-commerce: Leveraging online platforms to reach broader markets and streamline sales processes.
- Digital Marketing: Using digital channels like social media, email, and search engines to promote products and engage with customers.
Globalization

Globalization has transformed the business landscape by opening up international markets. Key considerations include:
- Cross-Border Trade: Engaging in import and export to expand market reach.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Understanding and respecting cultural differences to succeed in diverse markets.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to international laws and regulations governing trade and business practices.
- Global Supply Chain Management: Coordinating production, logistics, and distribution across multiple countries.
Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)

Modern businesses are increasingly focusing on sustainability and CSR:
- Sustainability: Implementing practices that minimize environmental impact and promote resource conservation.
- CSR: Engaging in ethical practices and contributing to societal well-being, such as community outreach and fair labor practices.
- Green Business: Developing eco-friendly products and adopting sustainable business models.
- Triple Bottom Line: Measuring success based on social, environmental, and financial performance.
Future Trends in Business

The future of business is shaped by emerging trends and innovations:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Automating processes and enhancing decision-making through machine learning and data analytics.
- Blockchain: Ensuring transparency and security in transactions and supply chains.
- Remote Work: Adapting to the growing trend of telecommuting and virtual teams.
- Gig Economy: Navigating the rise of freelance and contract work as part of the workforce.
- Sustainable Development: Focusing on long-term ecological balance and social equity.
Business Insights, Strategies and Innovation

This aspect explores deeper into specific aspects of business, each offering a focused perspective on different areas of interest:
1. Entrepreneurship
- Starting a Business: Steps to launch a new business, including business plan development, legal considerations, and funding.
- Startup Ecosystem: The role of incubators, accelerators, and venture capital in supporting new ventures.
- Scaling a Business: Strategies for growth, including market expansion, scaling operations, and managing resources.
2. Marketing and Branding
- Digital Marketing: Techniques and tools for online marketing, including SEO, social media marketing, and email campaigns.
- Brand Management: Building and maintaining a strong brand identity and reputation.
- Consumer Psychology: Understanding how consumers think and make purchasing decisions.
3. Financial Management
- Investment Strategies: Approaches to investing in stocks, bonds, real estate, and other assets.
- Corporate Finance: Managing a company’s finances, including capital structure, funding, and financial planning.
- Financial Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating financial risks through various tools and strategies.
4. Human Resources and Organizational Behavior
- Talent Acquisition: Strategies for recruiting and retaining top talent.
- Leadership and Management: Effective leadership styles and management practices.
- Employee Engagement and Culture: Building a positive organizational culture and fostering employee engagement.
5. Operations and Supply Chain Management
- Lean Manufacturing: Principles of lean production to minimize waste and maximize efficiency.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Strategies for improving supply chain performance and logistics.
- Quality Management: Ensuring product and service quality through standards and continuous improvement.
6. Business Ethics and Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Ethical business practices and their impact on society and the environment.
- Corporate Governance: Frameworks and policies for effective management and accountability in organizations.
- Ethical Dilemmas in Business: Common ethical issues and how to address them.
7. Global Business and International Trade
- International Business Strategies: Approaches to entering and competing in global markets.
- Trade Policies and Regulations: Understanding international trade agreements, tariffs, and regulations.
- Cross-Cultural Management: Managing and leading teams across different cultures and regions.
8. Technology and Innovation
- Emerging Technologies: Impact of AI, blockchain, IoT, and other technologies on business.
- Innovation Management: Processes for fostering innovation within an organization.
- Tech Startups: Challenges and opportunities for technology-driven startups.
9. Sustainability and Green Business
- Sustainable Business Practices: Implementing eco-friendly practices in operations and supply chains.
- Green Marketing: Promoting sustainable products and services.
- Impact Investing: Investments made with the intention to generate social and environmental impact alongside a financial return.
10. Economics and Business Environment
- Macroeconomic Factors: Understanding how economic indicators like GDP, inflation, and unemployment affect businesses.
- Microeconomics in Business: The application of microeconomic principles to business decisions.
- Regulatory Environment: Navigating laws and regulations that impact business operations.
The Impact of Business on Society

Business plays a pivotal role in shaping modern society. From job creation and economic growth to innovation and social development, businesses influence nearly every aspect of our daily lives. In this article, we will explore the multifaceted impact of business on society, highlighting both the positive contributions and the challenges it presents. Through a detailed examination, we aim to understand how businesses can drive progress and foster a better world.
Economic Growth and Development

To begin with, businesses are fundamental drivers of economic growth. They create jobs, which in turn, increases income levels and enhances the standard of living for individuals. Furthermore, businesses contribute significantly to the gross domestic product (GDP) of a nation, thereby bolstering the economy. For instance, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are often referred to as the backbone of the economy due to their role in job creation and economic diversification.
Moreover, businesses stimulate economic development by investing in infrastructure, such as transportation, communication, and utilities. These investments not only support the operations of the businesses themselves but also improve the quality of life for the broader community. Consequently, communities with thriving businesses tend to have better facilities and services.
Innovation and Technological Advancement

In addition to economic contributions, businesses drive innovation and technological advancement. Companies invest heavily in research and development (R&D) to create new products and improve existing ones. This relentless pursuit of innovation leads to breakthroughs that can transform industries and enhance daily life. For example, advancements in medical technology have significantly improved healthcare outcomes, while innovations in information technology have revolutionized communication and access to information.
Furthermore, the competitive nature of business encourages continuous improvement and adaptation. Companies that fail to innovate risk becoming obsolete, which incentivizes them to stay ahead of trends and technological developments. As a result, society benefits from a constant stream of new and improved products and services.
Social Contributions and Corporate Social Responsibility

Moreover, businesses play a crucial role in social development through their corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives. CSR refers to the efforts made by companies to contribute positively to society beyond their profit-driven motives. These initiatives can take various forms, including environmental sustainability programs, philanthropy, and community engagement.
For instance, many businesses implement sustainable practices to reduce their environmental footprint, such as using renewable energy sources or reducing waste. These efforts help protect the environment and promote a more sustainable future. Additionally, businesses often engage in philanthropic activities, such as donating to charities, supporting education, and providing disaster relief. By doing so, they address social issues and contribute to the well-being of the communities in which they operate.
Employment and Skill Development

Another significant impact of businesses on society is through employment and skill development. Businesses provide millions of jobs worldwide, offering individuals the means to support themselves and their families. Employment opportunities contribute to social stability and reduce poverty levels.
Furthermore, businesses invest in the development of their workforce through training and education programs. These initiatives help employees acquire new skills and improve their existing ones, enhancing their employability and career prospects. Consequently, a well-trained workforce is better equipped to meet the demands of a rapidly changing job market.
Challenges and Criticisms

However, it is important to acknowledge that the impact of business on society is not entirely positive. There are several challenges and criticisms associated with business practices that need to be addressed.
First, businesses can contribute to economic inequality. While they create wealth and job opportunities, the distribution of these benefits is often uneven. High-income individuals and executives may receive disproportionately large rewards compared to lower-income workers, exacerbating income inequality.
Second, some business practices can have negative environmental impacts. Industrial activities, for instance, can lead to pollution, deforestation, and depletion of natural resources. While many companies are adopting more sustainable practices, there is still a significant environmental cost associated with certain business operations.
Lastly, businesses can sometimes prioritize profit over ethical considerations. This can lead to issues such as labor exploitation, unsafe working conditions, and the production of harmful products. It is essential for businesses to operate ethically and for regulatory bodies to enforce standards that protect workers and consumers.
The Role of Business Sectors in Governance and Society
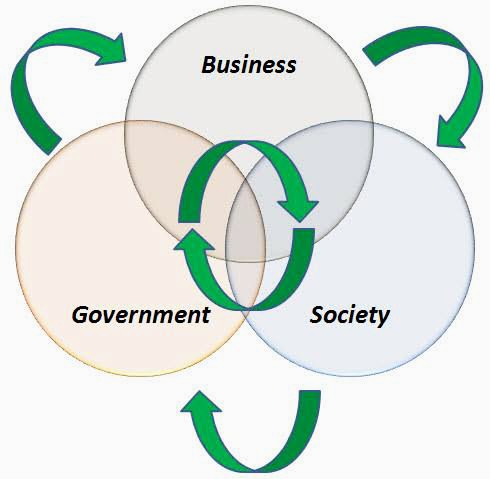
The interaction between business sectors, governance, and society is integral to the development and stability of modern economies. Business sectors not only contribute to economic prosperity but also influence social policies and environmental sustainability. This article explores how different business sectors impact governance and society, highlighting their roles in economic stability, social development, policy formation, environmental sustainability, and ethical standards.
Social Development and Community Engagement

Moreover, business sectors play a substantial role in social development and community engagement. Companies frequently undertake corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives, which benefit local communities in numerous ways. For example, businesses in the retail and hospitality sectors often support local charities and community projects, providing financial resources and volunteer efforts. These initiatives not only improve the social fabric of communities but also enhance the reputation and brand loyalty of the businesses involved. Thus, through active community engagement, business sectors contribute to social cohesion and improved quality of life.
Policy Formation and Governance

In addition, business sectors have a significant influence on policy formation and governance. Industry leaders and trade associations often collaborate with government bodies to shape policies that affect economic and social landscapes. For instance, the technology sector frequently engages with policymakers to develop regulations that foster innovation while protecting consumer rights. Additionally, sectors such as healthcare and finance are heavily regulated, and businesses within these sectors work closely with regulators to ensure compliance and advocate for favorable legislative changes. As a result, the collaboration between business sectors and governance bodies ensures that policies are well-informed and balanced, promoting sustainable development.
Environmental Sustainability and Innovation

Furthermore, business sectors are increasingly focusing on environmental sustainability and innovation. The energy and automotive sectors, for example, are at the forefront of developing green technologies and sustainable practices to combat climate change. Companies in these sectors invest in renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, and develop energy-efficient products to reduce their carbon footprint. Moreover, the agricultural sector adopts sustainable farming practices to ensure food security and environmental conservation. Consequently, the commitment of business sectors to environmental sustainability drives technological advancements and promotes a greener, more sustainable future.
Ethical Standards and Corporate Governance
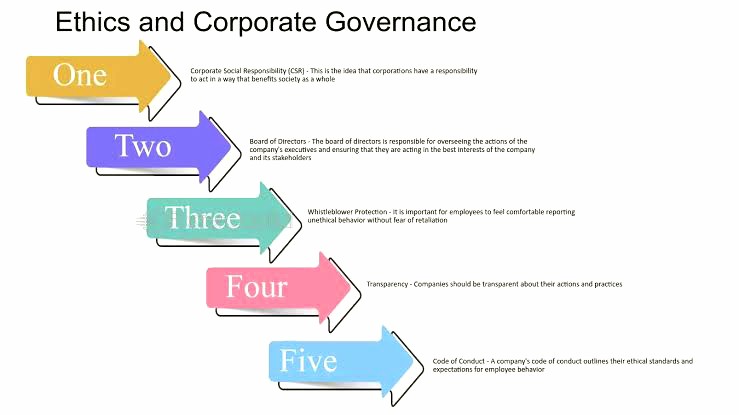
Lastly, the adherence to ethical standards and sound corporate governance within business sectors is paramount. Companies are expected to operate with integrity, transparency, and accountability, which are essential for maintaining public trust and investor confidence. The financial sector, for instance, has stringent regulations to prevent fraud and ensure ethical conduct. Similarly, the technology sector faces scrutiny regarding data privacy and ethical use of artificial intelligence. By upholding high ethical standards, businesses not only safeguard their reputation but also contribute to a fair and just society.
Conclusion

Business is a dynamic and multifaceted field that requires a comprehensive understanding of various principles and practices. By mastering strategic management, market dynamics, financial management, and embracing innovation and sustainability, businesses can thrive and contribute to economic and social progress. As the business environment continues to evolve, staying informed about emerging trends and adapting to change will be key to long-term success. Click for more Business Insights
Related Topics
Best Business Ideas to Make Money
Amazon: A Top E-commerce Company



This article about business is really helpful, educational and inspiring to those who want to venture into business.