Cancer: Definition, Types, Causes, Symptoms and Prevention
Cancer presents one of the most formidable health challenges globally, affecting millions of lives each year. This article examines the complexity of cancer, covering its definition, types, causes, symptoms and prevention strategies. Understanding these aspects is crucial for effectively managing and preventing this complex disease.
Definition of Cancer
It refers to a group of diseases characterized by uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells. These cells can invade nearby tissues and organs, disrupting their normal functions. The development of cancer often begins with genetic mutations that cause normal cells to transform into cancerous cells. These mutations can be inherited or acquired due to exposure to carcinogens or other factors.
Types of Cancer
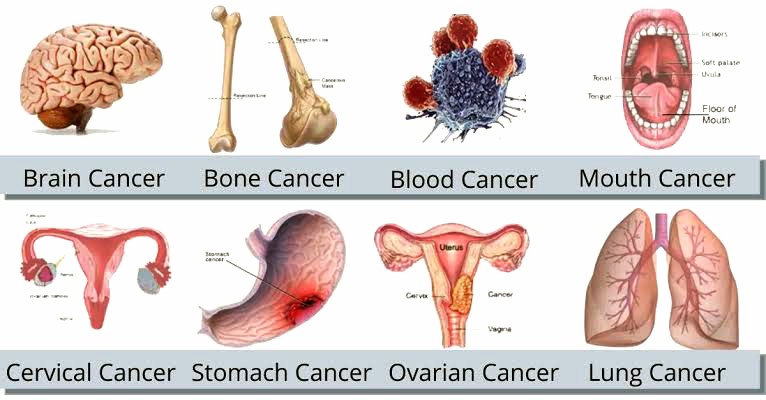
It can arise from different types of cells in the body, leading to various forms of the disease:
- Carcinomas: Originate in epithelial cells, which cover the surfaces of organs, glands, and body structures. Common examples include lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, and colorectal cancer.
- Sarcomas: Develop from connective tissues such as bones, muscles, cartilage, and blood vessels. They are less common than carcinomas but can be highly aggressive.
- Leukemias: Start in blood-forming tissues like the bone marrow and result in the overproduction of abnormal white blood cells. These cells may crowd out normal blood cells, leading to problems such as anemia, bleeding, and infection.
- Lymphomas: Affect the lymphatic system, which is part of the body’s immune system. They typically start in lymph nodes and lymphatic tissues and can spread to other organs.
- Central Nervous System Cancers: Occur in the brain and spinal cord and can affect vital functions due to their location.
Each type of cancer has distinct characteristics, treatment approaches, and prognoses. Understanding the specific type of cancer is crucial for developing personalized treatment plans.
Causes of Cancer
The development of cancer results from a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors:
- Genetic Factors: Inherited genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations associated with breast and ovarian cancers, can increase the risk of developing it. Moreover, genetic factors interact with environmental and lifestyle aspects.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to carcinogens such as tobacco smoke, ultraviolet radiation from the sun or tanning beds, asbestos fibers, and certain chemicals (e.g., benzene, formaldehyde) can trigger genetic mutations and promote cancer’s development. Furthermore, environmental factors may act synergistically with genetic predispositions.
- Lifestyle Factors: Unhealthy habits such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, a diet high in processed foods and low in fruits and vegetables, lack of physical activity, and being overweight or obese are associated with an increased risk of cancer. Additionally, lifestyle choices play a significant role in cancer’s prevention.
- Chronic inflammation, infections (e.g., human papillomavirus [HPV], Helicobacter pylori [H. pylori]), and hormonal factors (e.g., estrogen exposure in breast cancers) also play roles in the development of certain cancers.
Symptoms of Cancer
The signs and symptoms of cancer vary depending on the type, location, and stage of the disease. Early detection can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Common symptoms include:
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant and unintended weight loss can indicate several types of cancer, including pancreatic, stomach, esophageal, and lung cancers. Furthermore, sudden weight loss could be the first sign of it.
- Persistent Cough or Hoarseness: A persistent cough or hoarseness that does not resolve can be a sign of lung or throat cancers. Hence, persistent hoarseness may indicate cancer of the larynx.
- Changes in Bowel or Bladder Habits: Changes in bowel habits (e.g., diarrhea, constipation) or urinary habits (e.g., frequent urination, blood in urine) can indicate colorectal, bladder, or prostate cancers. Additionally, changes in bowel habits that persist may signal colon cancer.
- Fatigue: Persistent fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest can be a symptom of leukemia, colon cancer, or other cancers that cause blood loss or interfere with hormone levels. In addition, fatigue could be a sign of it.
Other symptoms may include unusual bleeding or discharge, persistent pain, lumps or thickening in the breast or other parts of the body, and skin changes such as a new mole or changes in an existing mole.
Prevention Strategies

Preventing cancer involves reducing exposure to risk factors and adopting healthy behaviors:
- Tobacco Control: Avoiding tobacco products and secondhand smoke is crucial, as smoking is linked to multiple types of cancer, including lung, throat, mouth, and bladder cancers. Additionally, quitting smoking can decrease the risk of it.
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of it. Specific dietary factors, such as limiting red and processed meats and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, are associated with a lower risk of certain cancers. Moreover, adopting a healthy diet can reduce cancer risk.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity can reduce the risk of several types of cancer, including breast, colon, and endometrial cancers. Furthermore, regular exercise is linked to lower its rates.
- UV Protection: Minimizing exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun and tanning beds, wearing protective clothing, and using sunscreen with a high SPF can reduce the risk of skin cancer. Consequently, protecting the skin from UV radiation is crucial in preventing skin cancer.
- Vaccination: Vaccines such as the HPV vaccine (for cervical, anal, and other HPV-related cancers) and the Hepatitis B vaccine (for liver cancer) can prevent infections that are associated with an increased risk of it. Moreover, vaccination is an effective strategy for preventing certain cancers.
Early detection through regular screening is also crucial for certain types of cancer. Screening tests such as mammograms, Pap tests, colonoscopies, and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests can detect it at an early stage when treatment is most effective.
Current Research and Treatment Advances
Advances in its research have improved our understanding of the molecular and genetic basis of cancer, as well as the development of targeted therapies and immunotherapies. These treatments aim to selectively target cancer cells while minimizing damage to normal cells, offering new hope for patients with advanced or difficult-to-treat cancers.
Immunotherapy equip the body’s immune system to fight it and has shown promising results in treating certain types. These include melanoma, lung cancer, and some types of lymphoma, highlighting the potential of immunotherapy in cancer’s treatment. Precision medicine, such as genomic testing to identify specific genetic mutations, allows for personalized treatment strategies. Tailoring treatment to individual patients’ genetic profiles can improve outcomes and target cancer more effectively.
Supportive Care and Quality of Life
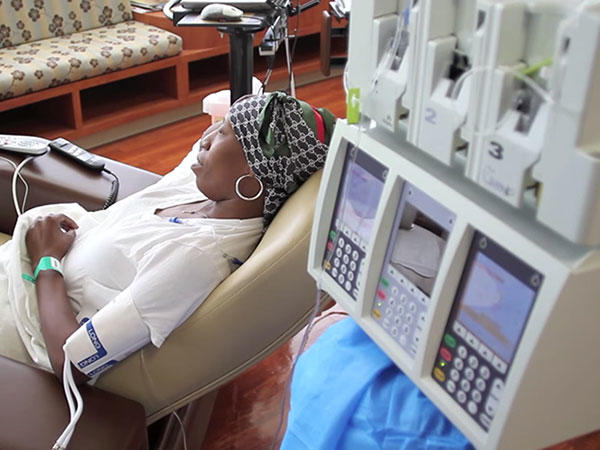
Managing it involves treating the disease and addressing the physical, emotional, and practical challenges faced by patients and families. Supportive care services, including palliative care and symptom management, aim to improve quality of life by alleviating pain. Managing side effects of treatment and providing emotional support are also crucial aspects of supportive care services for cancer patients.
Conclusion

In conclusion, it is a complex and multifaceted disease that requires a comprehensive approach to prevention and treatment. Understanding the definition, types, causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies helps individuals take proactive steps to reduce cancer’s risk. Improving outcomes if diagnosed requires early detection and a thorough understanding of cancer’s complexities and treatment options. Continued research, public awareness, and advancements in cancer’s care remain essential in the ongoing fight against this challenging disease.
Related Topics
Cholera Outbreak in Nigeria: Rising Death Toll and Vaccine Shortage



Nice health article, one can know the cause of cancer and how to prevent it.
Wow this is very helpful