
SEL: The Importance of Social-Emotional Learning

Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) is increasingly recognized as a crucial component of education. It focuses on developing skills that enable individuals to understand and manage emotions, set and achieve positive goals, feel and show empathy for others, establish and maintain positive relationships, and make responsible decisions. Additionally, SEL helps students build resilience and enhances their overall well-being.
What is Social-Emotional Learning (SEL)?

At its core, Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) encompasses a range of competencies that contribute to personal and interpersonal success. These include:
1. Self-Awareness
Self-awareness involves recognizing one’s own emotions and understanding how they influence thoughts and behavior. Additionally, it includes awareness of strengths, weaknesses, values, and goals. Moreover, this foundational skill allows individuals to sail through their emotional landscapes with greater clarity and purpose.
2. Self-Management
Self-management involves effectively regulating emotions, thoughts, and behaviors in different situations. It encompasses skills such as impulse control, stress management, goal setting, and perseverance. Furthermore, developing self-management skills helps individuals maintain focus, motivation, and resilience in the face of challenges.
3. Social Awareness
Social awareness involves understanding and empathizing with the emotions, perspectives, and experiences of others. Additionally, it includes sensitivity to cultural norms and contexts, as well as recognizing and appreciating diversity. Consequently, developing social awareness fosters empathy and promotes respectful interactions and relationships.
4. Relationship Skills
Relationship skills encompass communication, listening, cooperation, and conflict resolution. Moreover, these skills enable individuals to build and maintain healthy relationships with peers, family members, teachers, and the broader community. As a result, effective relationship skills contribute to a positive social environment and support collaborative efforts.
5. Responsible Decision-Making
Responsible decision-making involves making ethical and constructive choices about personal behavior and social interactions. It requires considering the well-being of oneself and others, as well as evaluating consequences and taking accountability for actions. Furthermore, developing responsible decision-making skills promotes integrity, ethical behavior, and positive contributions to society.
Benefits of Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) in Education

1. Academic Performance
Research consistently demonstrates a positive connection between SEL and academic achievement. Specifically, when students develop SEL competencies, they often exhibit improved focus, motivation, and academic engagement. Consequently, these skills enhance their ability to set and achieve academic goals, manage time effectively, and persevere through challenges.
2. Behavioral Outcomes
SEL programs significantly contribute to improved behavioral outcomes in schools. For instance, students who participate in Social-Emotional Learning initiatives demonstrate reduced behavioral issues such as aggression, bullying, and disciplinary incidents. Additionally, by promoting self-regulation and social competence, SEL helps create a positive school climate conducive to learning and personal growth.
3. Long-term Well-being
Beyond academic and behavioral benefits, SEL also equips individuals with skills that support long-term well-being and success. Specifically, these skills include emotional resilience, effective communication, adaptive coping strategies, and the ability to form meaningful relationships. By nurturing these competencies during childhood and adolescence, SEL ultimately lays a foundation for lifelong health, happiness, and positive social outcomes.
Implementing Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) Programs
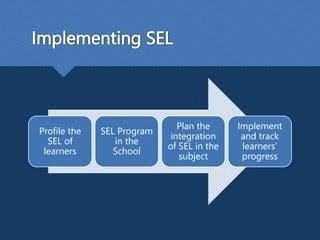
1. Integration into Curriculum
Successful implementation of SEL requires integrating Social-Emotional Learning practices into the core curriculum and daily routines of schools. By embedding Social-Emotional Learning into subjects such as language arts, social studies, and even mathematics, educators can reinforce SEL competencies while supporting academic learning. This comprehensive approach helps students see the relevance of Social-Emotional Learning in various aspects of their educational experience.
2. Teacher Training and Support
Educators play a critical role in fostering SEL competencies among students. Training teachers in Social-Emotional Learning principles and practices equips them with the knowledge and skills needed to create a supportive classroom environment. Professional development opportunities allow educators to learn effective Social-Emotional Learning strategies, integrate SEL into instructional practices, and address the social and emotional needs of their students.
3. Collaboration with Families and Communities
Collaboration with families and communities enhances the impact of Social-Emotional Learning initiatives. Engaging parents, caregivers, and community members in discussions about SEL fosters a shared understanding of its importance and benefits. By involving families in Social-Emotional Learning activities and providing resources for supporting SEL at home, schools strengthen the continuity of SEL learning between school and community settings.
Challenges and Considerations

1. Resource Allocation
One of the primary challenges in implementing effective SEL programs is securing adequate resources. This includes funding for curriculum materials, professional development, and support staff dedicated to Social-Emotional Learning initiatives. Schools may face competing priorities for limited resources, making strategic planning and advocacy essential for sustaining SEL efforts.
2. Measurement and Evaluation
Assessing the impact of Social-Emotional Learning programs requires reliable measurement tools and evaluation frameworks. Traditional academic assessments may not capture the full range of SEL competencies. Schools need to develop and implement assessment strategies that measure changes in students’ social and emotional skills over time. These assessments inform programmatic adjustments and demonstrate the value of SEL to stakeholders.
The Application of Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) in Society

Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) is increasingly gaining recognition not only in schools but also throughout broader society. Its principles of developing emotional intelligence, empathy, and responsible decision-making significantly enhance community well-being and personal growth across various contexts.
Understanding SEL
To begin with, SEL focuses on five core competencies: self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making. These competencies collectively help individuals understand and manage their emotions, set and achieve goals, and build positive relationships.
SEL in Schools
Firstly, the implementation of SEL in educational settings effectively lays the groundwork for broader societal application. Schools that integrate Social-Emotional Learning create environments where students learn to communicate effectively, resolve conflicts, and collaborate with peers. As a result, students equipped with Social-Emotional Learning skills are more likely to contribute positively to society.
Expanding Beyond the Classroom
Moreover, the application of SEL extends well beyond the classroom. In the workplace, for instance, Social-Emotional Learning principles can significantly enhance teamwork and leadership. Employees with strong social-emotional skills are better able to sail through interpersonal dynamics, which leads to improved collaboration and productivity.
In addition, Social-Emotional Learning initiatives in community settings address social issues such as bullying and violence. Programs that promote empathy and conflict resolution contribute to safer and more inclusive communities. For example, community centers and youth programs often incorporate SEL to help young people develop resilience and a sense of belonging.
Benefits of SEL in Society
The benefits of SEL in society are manifold. Firstly, it fosters emotional intelligence, which is crucial for personal and professional success. Individuals with high emotional intelligence are better equipped to manage stress, communicate effectively, and maintain healthy relationships.
Furthermore, SEL actively promotes mental health. By teaching individuals to recognize and regulate their emotions, Social-Emotional Learning reduces anxiety and depression, leading to improved overall well-being. In turn, this enhancement of community health reduces the burden on mental health services.
Additionally, SEL contributes to social cohesion. When individuals possess skills like empathy and active listening, they are more likely to engage in constructive dialogue, thereby reducing polarization and fostering mutual understanding.
Challenges and Considerations
Nevertheless, implementing Social-Emotional Learning on a societal level presents several challenges. One major obstacle involves ensuring that programs are inclusive and culturally relevant. SEL must be adapted to meet the diverse needs of various communities, taking into account cultural values and practices.
Moreover, there is often a lack of awareness or understanding of SEL’s importance outside educational settings. To address this, advocacy and education are crucial. Community leaders and organizations play vital roles in promoting the benefits of SEL and integrating its principles into various programs and initiatives.
Overall

The application of Social-Emotional Learning in society is essential for fostering emotional intelligence, empathy, and social cohesion. Although challenges exist, the widespread benefits of Social-Emotional Learning—such as enhanced mental health, improved relationships, and overall community well-being—are undeniable. By prioritizing Social-Emotional Learning, society can create environments where individuals thrive both personally and collectively, ultimately leading to a more compassionate and connected world.
In summary, Social-Emotional Learning is a vital component of education that promotes integral development, equipping individuals with essential skills for personal and interpersonal success. By cultivating self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making, SEL prepares students to thrive academically, socially, and emotionally. As schools continue to prioritize Social-Emotional Learning initiatives, they contribute to creating supportive learning environments where all students can reach their full potential.
Related Topics
Microlearning: Definition, Examples and Platforms
Understanding Stress: Comprehensive Insights into Causes, Effects and Management
An Article on Artificial Intelligence



Nice article, this is really educational and inspiring.