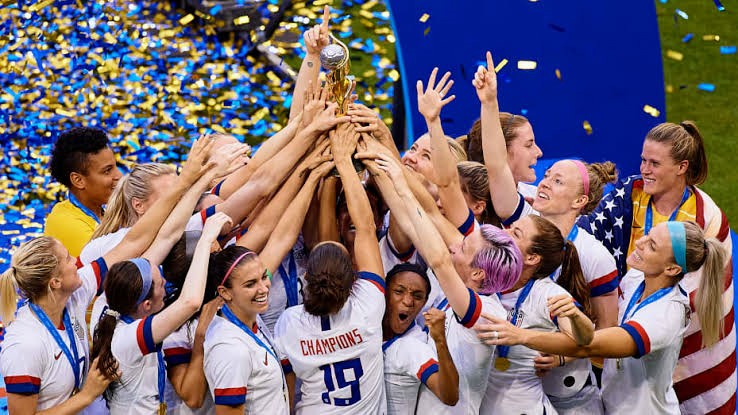

The Women’s World Cup

The Women’s World Cup, a pinnacle event in women’s sports, has significantly transformed the landscape of women’s soccer since its inception. Initially met with skepticism and marginalization, the tournament evolved into a celebrated global event, drawing millions of viewers and inspiring generations of female athletes. This article feature into the history, evolution, and societal impact of the Women’s World Cup, highlighting its journey from humble beginnings to global acclaim.
Historical Background
The idea of a women’s soccer world championship first materialized in 1991. Despite soccer’s longstanding popularity, opportunities for women in the sport remained minimal. The inaugural tournament in China featured 12 teams. Nevertheless, though it lacked the fanfare of its male counterpart, it marked a crucial step forward for women’s sports.
Growth and Development
As the years progressed, the Women’s World Cup grew both in scope and recognition. In 1999, the tournament expanded to 16 teams, and the final in the United States at the Rose Bowl attracted a record-breaking attendance of over 90,000 spectators. Consequently, this particular edition is often cited as a turning point, significantly boosting the visibility and popularity of women’s soccer.
Subsequent tournaments continued this trend. By the 2015 World Cup in Canada, the tournament featured 24 teams, demonstrating increased global participation and competitiveness. Furthermore, FIFA’s commitment to gender equality and investment in women’s soccer played a crucial role in this growth. The 2019 World Cup in France further exemplified this progress, with widespread media coverage, high-quality broadcasts, and increased prize money for the teams.
Societal Impact
The Women’s World Cup profoundly impacts society, influencing perceptions of women in sports and beyond. Firstly, the visibility of female athletes on such a large stage challenges stereotypes and encourages young girls to pursue sports. The performances of athletes like Mia Hamm, Abby Wambach, and Megan Rapinoe transcend soccer, making them icons of women’s empowerment.
Moreover, the tournament sparks important conversations about gender equality in sports. Issues such as pay disparity, media coverage, and investment in women’s sports gain attention and prompt change. For instance, the U.S. Women’s National Team’s fight for equal pay brought significant public and legal scrutiny to the pay discrepancies between male and female athletes.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the progress, challenges remain. Disparities in pay, facilities, and support compared to men’s soccer persist. Furthermore, the development of women’s soccer in less affluent countries lags due to insufficient infrastructure and funding. However, awareness and advocacy continue to address these challenges.
Looking ahead, the future of the Women’s World Cup appears promising. Moreover, FIFA plans to expand the tournament further, aiming to increase participation and viewership. Additionally, the 2023 World Cup, co-hosted by Australia and New Zealand, promises to set new benchmarks in terms of organization, audience engagement, and competitive quality.
The History of the FIFA Women’s World Cup

The FIFA Women’s World Cup is an international football (soccer) tournament held every four years by FIFA (Fédération Internationale de Football Association). It began in 1991 and the most recent edition took place in 2019 in France, with the United States emerging as the champions. The next Women’s World Cup is scheduled for 2023 in Australia and New Zealand. This event marks a significant milestone for women’s football, highlighting top talent and increasing global interest in the sport.
The FIFA Women’s World Cup stands as the pinnacle of international women’s football, celebrating athletic excellence, determination, and the spirit of competition. Since its inception, the tournament has grown in popularity and prestige, showcasing the remarkable talent of female footballers worldwide. Here is a detailed overview of each tournament, its context, and its impact on the sport.
1991: The Inaugural Tournament in China
China hosted the first FIFA Women’s World Cup in 1991. This groundbreaking event marked a significant milestone for women’s football, providing a global stage for female athletes. The United States emerged victorious, setting a high standard for future competitions. This tournament proved that women’s football could draw international attention and foster competitive spirit.
1995: Norway Triumphs in Sweden
Four years later, Sweden hosted the second edition of the Women’s World Cup. Subsequently, Norway claimed the title, showcasing their dominance in the sport. This victory demonstrated the growing diversity in competitive women’s football, as different nations began to rise and challenge the established powers.
1999: A Landmark Event in the United States
The 1999 Women’s World Cup, held in the United States, is often remembered for its iconic moments and substantial media coverage. The United States clinched their second title in front of record-breaking crowds, with the final match against China drawing massive attention. Brandi Chastain’s winning penalty kick and subsequent celebration became emblematic of the tournament’s success and the burgeoning popularity of women’s football in America.
2003: Germany’s Ascendancy in the United States
Continuing the trend of holding the tournament in diverse locations, the 2003 Women’s World Cup took place again in the United States. Subsequently, Germany emerged victorious, marking the beginning of their dominance in women’s football. This win underscored Germany’s tactical prowess and solidified their reputation as a football powerhouse.
2007: Germany Retains the Title in China
In 2007, China once again hosted the Women’s World Cup. Consequently, Germany defended their title successfully, becoming the first team to win consecutive Women’s World Cups. Their performance demonstrated the depth of their squad and the effectiveness of their footballing strategy, reinforcing their status on the global stage.
2011: Japan’s Inspirational Victory in Germany
The 2011 Women’s World Cup in Germany was a poignant and memorable tournament. Moreover, Japan triumphed, securing their first World Cup title in the wake of the devastating earthquake and tsunami that struck their nation. This victory was not only a footballing achievement but also a symbol of resilience and hope for the Japanese people.
2015: United States Dominates in Canada
Canada hosted the 2015 Women’s World Cup, which saw the United States reclaim the title. The American team showcased their exceptional skills and determination, culminating in a commanding 5-2 victory over Japan in the final. This win further established the United States as a dominant force in women’s football, with stars like Carli Lloyd shining brightly on the world stage.
2019: The United States’ Fourth Triumph in France
In 2019, France hosted the Women’s World Cup, bringing together the best teams from around the world. The United States continued their reign of dominance, winning their fourth World Cup title. Their success was characterized by a blend of experienced players and emerging talents, reflecting the depth of their footballing culture.
2023: Spain’s Historic Victory in Australia and New Zealand
The 2023 Women’s World Cup, co-hosted by Australia and New Zealand, marked a significant chapter in the tournament’s history. Consequently, Spain emerged as the champions, winning their first Women’s World Cup. This victory highlighted the growing strength of European teams in women’s football and showcased the global spread of the sport.
In summary, the FIFA Women’s World Cup has evolved tremendously since its inception in 1991. Each tournament has contributed to the growing recognition and appreciation of women’s football, inspiring new generations of players and fans alike. As we look forward to future tournaments, the legacy of these past champions continues to shape the sport, driving it towards greater heights and broader horizons.
2024 Women’s World Cup Standings
The 2024 Women’s World Cup standings showcase fierce competition among the teams. Here are the key standings from the group stages:
1. Group A:
- Switzerland leads with 5 points, achieving one win and two draws.
- Norway follows closely with 4 points from one win, one draw, and one loss.
- New Zealand also holds 4 points but with a lesser goal difference.
- Philippines rounds out the group with 3 points from one win and two losses.
2. Group B:
- Australia tops the group with 6 points from two wins and one loss.
- Nigeria sits second with 5 points from one win and two draws.
- Canada gathers 4 points from one win, one draw, and one loss.
- Republic of Ireland remains last with 1 point from one draw and two losses.
3. Group C:
- Japan dominates with a perfect record of 3 wins, scoring 11 goals and conceding none.
- Spain follows with 6 points from two wins and one loss.
- Zambia earns 3 points from one win and two losses.
- Costa Rica records no points, losing all three matches.
4. Group D:
- England leads with 9 points from three wins.
- Denmark follows with 6 points from two wins and one loss.
- China accumulates 3 points from one win and two losses.
- Haiti sits at the bottom with no points.
5. Group E:
- Netherlands tops the group with 7 points from two wins and one draw.
- USA secures second place with 5 points from one win and two draws.
- Portugal garners 4 points from one win, one draw, and one loss.
- Vietnam holds no points from three losses.
These standings illustrate the intense nature of the tournament as teams compete for top positions to advance to the knockout stages. Additionally, for more detailed updates and full standings, visit the official websites of UEFA and FIFA.
The Women’s World Cup Brackets

The Women’s World Cup, organized by FIFA, features a structured competition format that showcases the world’s best female soccer teams. The tournament unfolds in stages, starting with the group phase and culminating in thrilling knockout rounds. This article provides a detailed exploration of how the Women’s World Cup brackets are structured, highlighting each stage’s significance and the transition from group play to intense single-elimination matches.
Group Stage: Testing Skill and Strategy
The journey begins with the group stage, where teams divide into several groups, typically labeled A to F. Each group consists of four teams, and they compete in a round-robin format. During this phase, every team plays against the others in their group, totaling three matches per team. The outcomes of these matches determine the group standings based on points awarded for wins and draws. Teams strive to secure their position in the rankings, aiming to advance to the knockout stage.
Advancing to Knockout Stage: Rising Above the Rest
As the group stage concludes, the top teams from each group secure their place in the knockout stage. In some instances, a few of the best-performing second-place teams also advance, adding an element of competitiveness and unpredictability to the brackets. The transition from group play to knockout matches marks a pivotal moment where teams must elevate their performance to survive and advance further in the tournament.
Knockout Stage: The Road to Glory
The knockout stage of the Women’s World Cup intensifies the competition, showcasing high-stakes matches characterized by single-elimination rules. Transitioning into the journey with the Round of 16, where 16 teams face off in decisive matches, each match becomes a battle of skill, strategy, and resilience as teams vie for a coveted spot in the quarter-finals.
Moving from the Round of 16, eight teams progress to the quarter-finals, setting the stage for even more exhilarating matchups. These quarter-final clashes are pivotal, with teams striving to secure a place among the final four contenders.
Women World Cup Fixtures

The Women’s World Cup fixtures start with the group stage, where teams play round-robin matches to determine who advances. Then, the tournament moves into the knockout phase with the Round of 16, followed by the quarterfinals and semifinals. A third-place play-off determines the bronze medalist, while the final decides the world champion. Each stage builds excitement, culminating in a showcase of top-tier women’s football.
FIFA Women’s World Cup Winners

Here’s a concise list of the FIFA Women’s World Cup winners since it began:
- 1991: United States
- 1995: Norway
- 1999: United States
- 2003: Germany
- 2007: Germany
- 2011: Japan
- 2015: United States
- 2019: United States
These countries have all claimed victory in the FIFA Women’s World Cup. Furthermore, if you want more detailed information or current standings, feel free to ask!
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Women’s World Cup has evolved significantly since 1991, symbolizing progress in women’s sports through growth, investment, and advocacy. It celebrates athletic excellence, champions gender equality, and inspires future generations, shaping both women’s soccer and societal attitudes toward women’s sports.


